Financial inclusion is a critical aspect of socioeconomic development, empowering individuals and communities to access and utilize financial services. The development of effective financial inclusion policies is crucial to create a supportive environment for individuals and businesses to participate fully in the financial system.
Financial Inclusion Policy Development

The process of developing financial inclusion policies involves several key steps:
- Assessment and Data Gathering: Conduct research to assess the existing financial inclusion landscape, including the barriers and challenges faced by underserved populations. Collect data on financial exclusion and identify potential target groups.
- Goal Setting: Establish clear and measurable goals for financial inclusion, such as increasing access to basic financial services, promoting savings and investment, and reducing financial vulnerability.
- Identification of Interventions: Explore and evaluate various policy interventions, including regulatory measures, incentives, and partnerships with financial institutions. Consider the feasibility and impact of potential interventions.
- Policy Design: Draft and finalize financial inclusion policies that outline the specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementation. Ensure alignment with other economic and social policies.
How do you create financial inclusion?
Creating financial inclusion involves a multi-faceted approach that addresses the various barriers to accessing and utilizing financial services. Some key strategies include:
- Improving Access to Financial Services:
- Expanding the physical and digital infrastructure of financial institutions to reach underserved areas.
- Promoting the use of innovative financial technologies (fintech) to provide affordable and accessible financial services.
- Encouraging the development of alternative financial service providers, such as microfinance institutions and mobile money operators.
- Enhancing Financial Literacy and Capability:
- Implementing financial education programs to improve the understanding of financial concepts and products.
- Providing targeted financial guidance and counseling to help individuals and small businesses make informed financial decisions.
- Leveraging digital platforms and social media to disseminate financial information and resources.
- Addressing Regulatory and Policy Barriers:
- Reviewing and reforming financial regulations to create an enabling environment for financial inclusion.
- Developing supportive policies that incentivize financial institutions to serve underserved populations.
- Ensuring consumer protection measures are in place to safeguard the rights and interests of financial service users.
- Fostering Partnerships and Collaboration:
- Engaging with a diverse range of stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, civil society organizations, and development partners.
- Facilitating public-private partnerships to leverage the resources and expertise of different sectors.
- Promoting cross-sector collaboration to address the multidimensional challenges of financial exclusion.
What is the Financial Inclusion Initiative Around the World?
Financial inclusion has become a global priority, with many countries and international organizations taking steps to promote access to financial services and financial well-being. Some notable financial inclusion initiatives around the world include:
- Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion (GPFI): Established by the G20 in 2010, the GPFI is a platform for peer learning, knowledge-sharing, and coordination among countries, standard-setting bodies, and other stakeholders.
- Alliance for Financial Inclusion (AFI): A global network of policymakers and regulators from developing and emerging countries, the AFI supports the development and implementation of financial inclusion policies and strategies.
- Maya Declaration: Launched in 2011, the Maya Declaration is a commitment by AFI members to implement measurable financial inclusion targets and policies.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): The United Nations’ SDGs include a specific target (SDG 8.10) to “strengthen the capacity of domestic financial institutions to encourage and expand access to banking, insurance and financial services for all.”
- World Bank Universal Financial Access 2020 Initiative: This initiative aims to ensure that all adults worldwide have access to a transaction account or electronic instrument to store money, send payments, and receive deposits by the year 2020.
What is the Financial Inclusion Agenda?
The financial inclusion agenda encompasses a broad range of objectives and initiatives aimed at improving access to and usage of financial services for underserved populations. The key components of the financial inclusion agenda include:
- Access to Basic Financial Services:
- Ensuring that individuals and small businesses have access to basic financial products, such as savings accounts, credit, insurance, and payment services.
- Promoting the establishment of physical and digital infrastructure, such as bank branches, ATMs, and mobile money platforms, in underserved areas.
- Financial Literacy and Capability:
- Developing and implementing financial education programs to improve people’s understanding of financial concepts and products.
- Empowering individuals to make informed financial decisions and manage their money effectively.
- Inclusive Financial Regulations and Policies:
- Reviewing and reforming financial regulations to create an enabling environment for financial inclusion.
- Developing supportive policies that incentivize financial institutions to serve underserved populations.
- Ensuring consumer protection measures are in place to safeguard the rights and interests of financial service users.
- Innovative Financial Technologies (Fintech):
- Leveraging digital technologies, such as mobile banking, digital wallets, and blockchain, to expand access to financial services.
- Promoting the development and adoption of fintech solutions that address the unique needs of underserved communities.
- Targeted Interventions for Vulnerable Groups:
- Designing and implementing policies and programs that address the specific financial inclusion challenges faced by women, youth, rural populations, and other marginalized groups.
- Promoting financial inclusion as a means to achieve broader social and economic development goals, such as poverty alleviation, gender equality, and financial resilience.
The financial inclusion agenda is a dynamic and evolving field, with ongoing efforts to adapt and refine strategies based on the unique contexts and needs of different countries and communities.
What is the National Financial Inclusion Strategy South Sudan?
The National Financial Inclusion Strategy (NFIS) of South Sudan is a comprehensive plan aimed at improving access to and usage of financial services for the country’s underserved population. The key components of the NFIS include:
- Vision and Objectives:
- The NFIS vision is to “create a financially inclusive ecosystem that provides accessible, affordable, and appropriate financial services to all individuals and enterprises in South Sudan.”
- The strategy sets specific targets, such as increasing the percentage of adults with access to formal financial services from 15% to 40% by 2025.
- Thematic Pillars:
- The NFIS is structured around four thematic pillars: Access to Financial Services, Usage of Financial Services, Financial Capability, and Financial Consumer Protection.
- Each pillar outlines specific strategies and interventions to address the barriers and challenges within that area.
- Targeted Initiatives:
- The NFIS includes targeted initiatives to address the needs of priority segments, such as women, youth, and small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- These initiatives focus on expanding access to credit, savings, insurance, and other financial products tailored to the unique requirements of these groups.
- Institutional Arrangements:
- The strategy establishes a National Financial Inclusion Council, chaired by the Minister of Finance and Planning, to provide overall guidance and oversight for the NFIS implementation.
- The Bank of South Sudan is designated as the lead implementing agency, responsible for coordinating efforts across various stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- The NFIS includes a comprehensive monitoring and evaluation framework to track progress, measure impact, and inform policy adjustments.
- Regular reporting and data collection mechanisms are put in place to ensure the ongoing assessment of the strategy’s effectiveness.
The National Financial Inclusion Strategy of South Sudan represents a crucial step in the country’s efforts to address financial exclusion and promote sustainable economic development through improved access to financial services.
Financial Inclusion Policy Development Framework
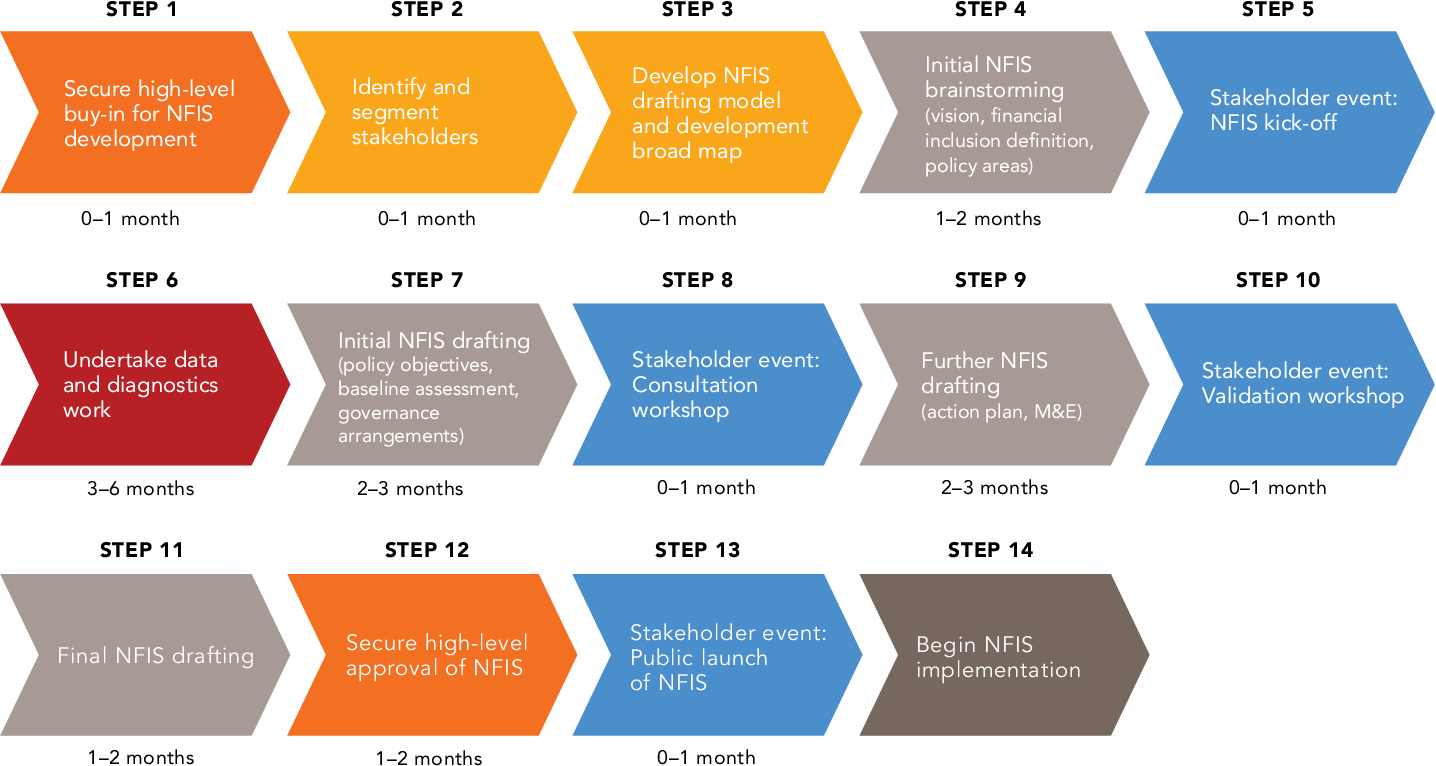
The development of effective financial inclusion policies can be guided by a comprehensive framework that addresses the key elements of the policy-making process. This framework typically includes the following components:
1. Situational Analysis
- Conduct a thorough assessment of the current financial inclusion landscape, including the barriers and challenges faced by underserved populations.
- Gather and analyze relevant data on financial exclusion, such as access to financial services, usage patterns, and demographic characteristics of the unserved and underserved.
- Identify the target groups and priority segments for financial inclusion interventions, such as low-income individuals, rural communities, women, and small businesses.
2. Stakeholder Engagement
- Engage with a diverse range of stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, civil society organizations, and development partners.
- Facilitate consultations and dialogues to gather insights, identify priorities, and build consensus on the financial inclusion agenda.
- Ensure the participation of underserved communities and vulnerable groups in the policy development process.
3. Policy Objectives and Targets
- Establish clear and measurable objectives for financial inclusion, such as increasing access to basic financial services, promoting savings and investment, and reducing financial vulnerability.
- Set specific targets and timelines to track progress and evaluate the effectiveness of the policy interventions.
- Align the financial inclusion objectives with broader economic, social, and sustainable development goals.
4. Policy Interventions
- Explore a range of policy interventions, including regulatory measures, incentives, and partnerships with financial institutions.
- Evaluate the feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and potential impact of each intervention.
- Prioritize interventions that address the identified barriers and challenges to financial inclusion.
5. Policy Design and Implementation
- Draft and finalize the financial inclusion policy, outlining the specific actions, responsibilities, and timelines for implementation.
- Ensure the policy is aligned with other relevant economic and social policies, and that it creates a supportive and enabling environment for financial inclusion.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan, including the allocation of resources, capacity-building initiatives, and stakeholder coordination mechanisms.
6. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Establish a robust monitoring and evaluation framework to track the progress and impact of the financial inclusion policy.
- Collect and analyze relevant data, including access, usage, and impact indicators, to inform policy adjustments and refinements.
- Regularly review and update the policy based on the findings of the monitoring and evaluation process.
By following this comprehensive framework, policymakers can develop and implement financial inclusion policies that are evidence-based, inclusive, and responsive to the evolving needs of underserved populations.
Financial Inclusion Policy Development Examples

To illustrate the practical application of financial inclusion policy development, here are two examples from different countries:
Example 1: Indonesia’s National Strategy for Financial Inclusion (SNKI)
Background: Indonesia has a large and diverse population, with significant variations in access to financial services across different regions and demographic groups. In 2016, the Indonesian government launched the National Strategy for Financial Inclusion (SNKI) to address these disparities and promote inclusive economic growth.
Key Components of the SNKI:
- Situational Analysis: The SNKI was developed based on a comprehensive assessment of the existing financial inclusion landscape, including data on access, usage, and barriers to financial services.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The policy-making process involved extensive consultations with government agencies, financial institutions, civil society organizations, and representatives from underserved communities.
- Policy Objectives and Targets: The SNKI set a goal of increasing the percentage of adults with access to formal financial services from 36% in 2014 to 75% by 2019.
- Policy Interventions: The strategy outlined a range of interventions, such as expanding financial infrastructure, promoting digital financial services, and strengthening financial literacy programs.
- Policy Design and Implementation: The SNKI was integrated with other economic and social policies, and a detailed implementation plan was developed, including the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: The SNKI established a comprehensive monitoring and evaluation framework, with regular data collection and reporting on key financial inclusion indicators.
Outcomes and Impact: The implementation of the SNKI has led to significant progress in financial inclusion in Indonesia. By 2019, the percentage of adults with access to formal financial services had reached 76%, exceeding the initial target.
Example 2: Nigeria’s National Financial Inclusion Strategy (NFIS)
Background: Nigeria has a large, growing, and underserved population, with significant disparities in access to financial services, particularly among rural and low-income communities. In 2012, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) and other stakeholders developed the National Financial Inclusion Strategy (NFIS) to address these challenges.
Key Components of the NFIS:
- Situational Analysis: The NFIS was informed by a detailed assessment of the financial inclusion landscape, including surveys and data collection on access, usage, and barriers to financial services.
- Stakeholder Engagement: The policy development process involved extensive consultations with a wide range of stakeholders, including government agencies, financial institutions, civil society organizations, and representatives from target communities.
- Policy Objectives and Targets: The NFIS set a goal of reducing the percentage of financially excluded adults from 46.3% in 2010 to 20% by 2020.
- Policy Interventions: The strategy outlined a comprehensive set of interventions, such as promoting the use of agent banking and digital financial services, strengthening financial literacy programs, and developing customized financial products for underserved groups.
- Policy Design and Implementation: The NFIS was aligned with other national development plans and policies, and a detailed implementation plan was developed, including the roles and responsibilities of different stakeholders.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: The NFIS established a robust monitoring and evaluation framework, with regular data collection, reporting, and policy adjustments based on the findings.
Outcomes and Impact: The implementation of the NFIS has contributed to significant progress in financial inclusion in Nigeria. By 2018, the percentage of financially excluded adults had been reduced to 36.8%, demonstrating the positive impact of the strategy.
These examples illustrate how the financial inclusion policy development framework can be applied in different country contexts, with tailored interventions and implementation approaches to address the unique challenges and priorities of each national financial inclusion agenda.
Conclusion

The development of effective financial inclusion policies is crucial to creating a supportive environment for individuals and businesses to participate fully in the financial system. By following a comprehensive framework that addresses key elements of the policy-making process, policymakers can design and implement financial inclusion policies that are evidence-based, inclusive, and responsive to the evolving needs of underserved populations.
The examples of Indonesia’s National Strategy for Financial Inclusion and Nigeria’s National Financial Inclusion Strategy demonstrate how the financial inclusion policy development framework can be applied in practice, leading to tangible progress in improving access to and usage of financial services. As the global financial inclusion agenda continues to evolve, the lessons and insights from these and other successful policy initiatives can inform and inspire the development of financial inclusion policies in other countries, contributing to the broader goal of inclusive and sustainable economic development.
wfriv.xyz